Introduction to State Machines
This week we'll cover the basics of state machines and how to utilize them in your project.
A State Machine is defined as a device that can be in a set number of stable conditions depending on its previous condition and on the present values of its inputs. In a game design context, it keeps track of what a game object is currently doing and capable of doing.
State machines can be most often and most importantly in the context of the player or enemy AI.
Lets use Minecraft as an example. Some examples of player state in Minecraft are walking/running, mining, attacking, interacting with objects, etc. We have to think about the context of when these states take place, and what a player can or cannot do when they are in each of the states. For example, when the player is using a consumable like food or a potion, they can still move around the environment but they can't attack/mine. When the player is interacting with the world, like a crafting table, they can neither move nor attack/mine. Using this example we can see that the state machine takes input and changes the state of the player, and what they can do accordingly.
State Machines can be represented by state diagrams. The one below is an example of a state machine for an enemy AI.
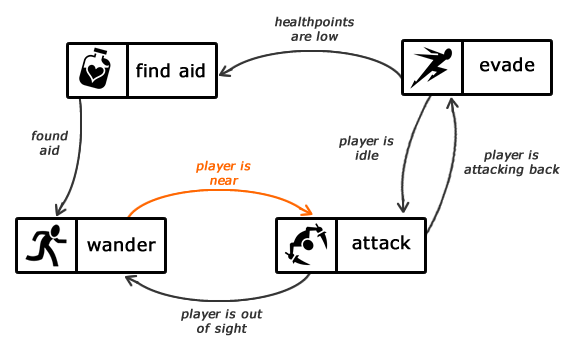
This state machine describes how a simple enemy should behave when looking for and fighting the player. The boxes are the different states describing what the enemy is doing when in that state and the arrows indicate which state they will transition to upon the specified input.
While they seem rather straight forward it is easy to create a state machine that is not as you intended. For example, if the enemy is on low health in the attacking state they will not seek out aid. It is important that you create ALL the transitions that could occur in the game.
To help give more of an example of what state machines look like in code, this is a state machine developed for one of the final projects last year.
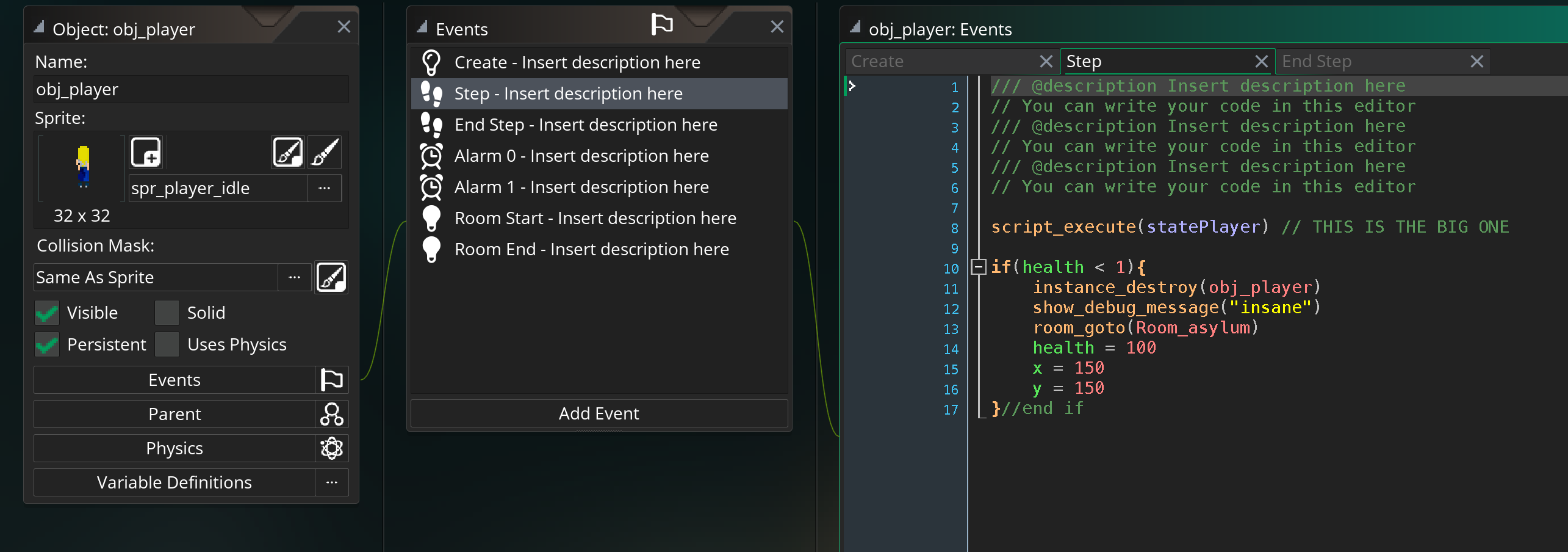
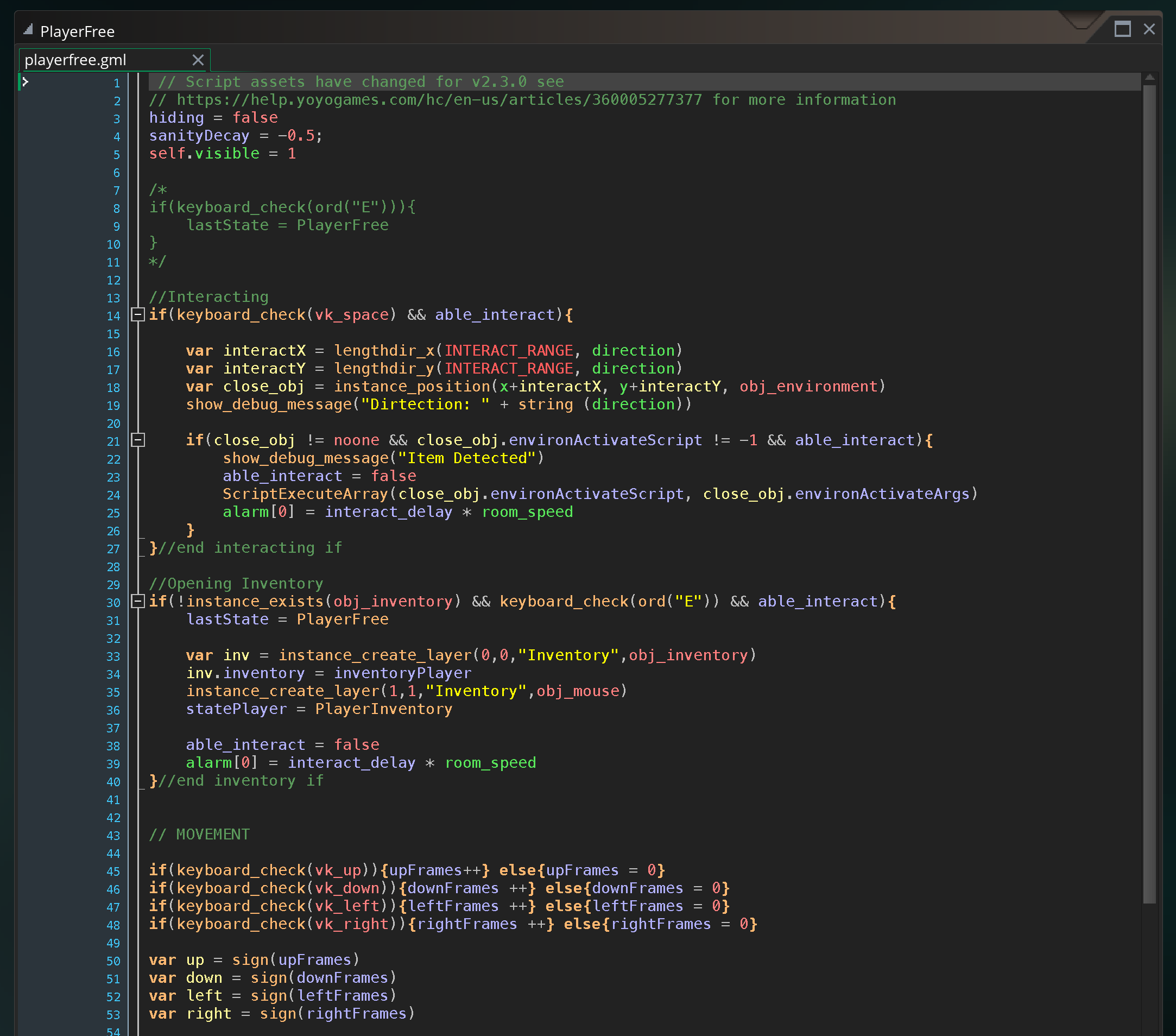
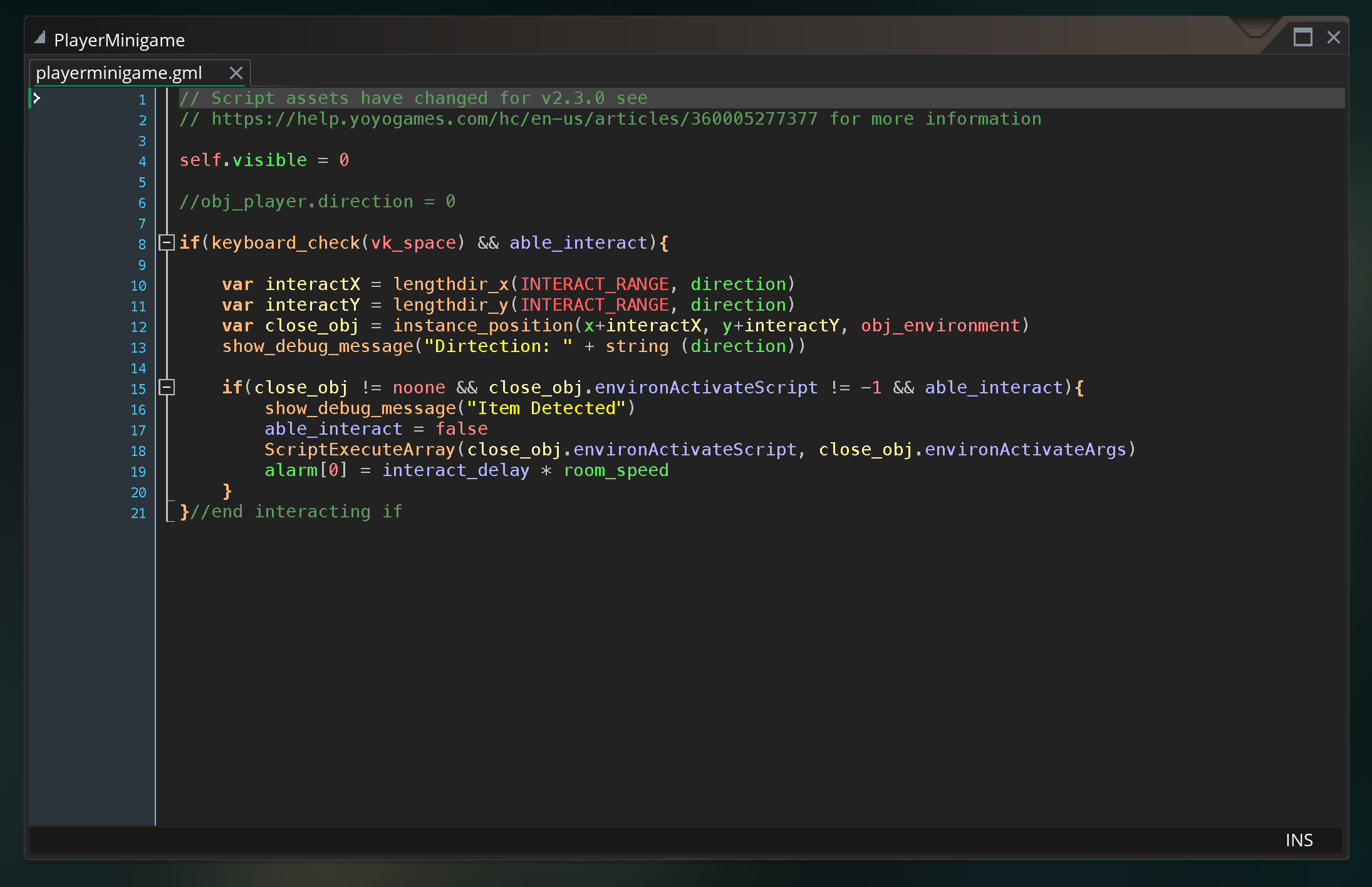
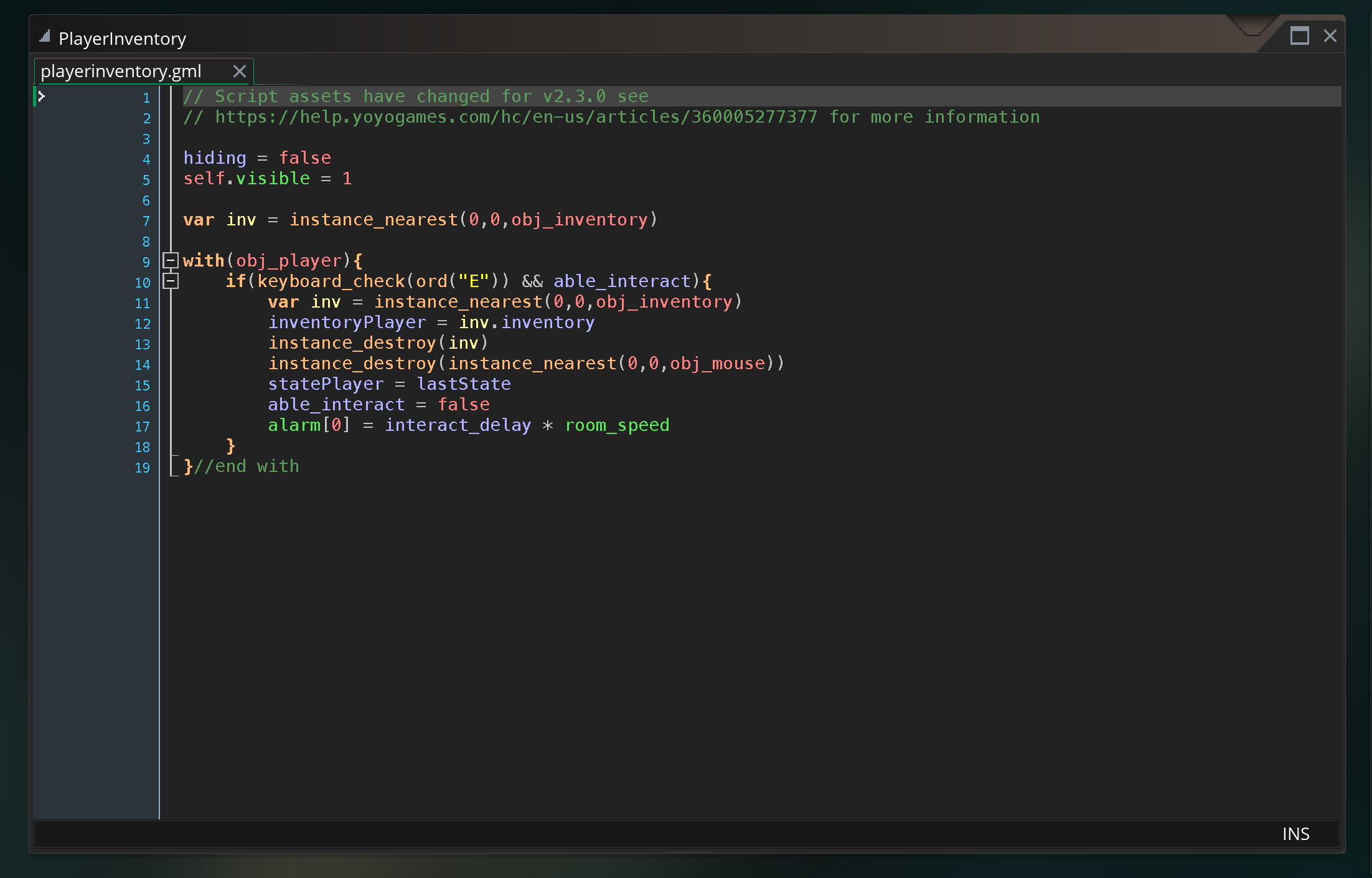
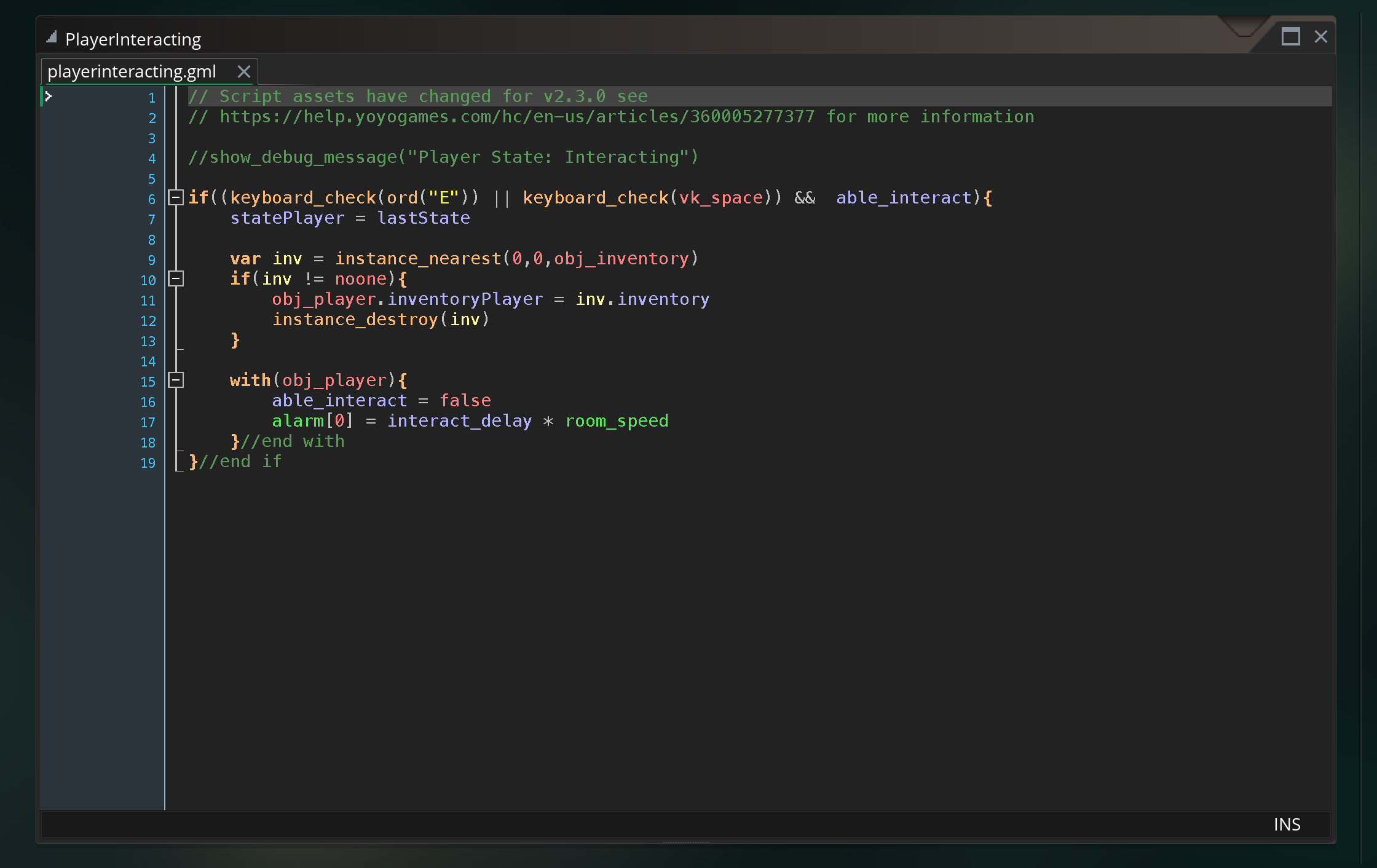
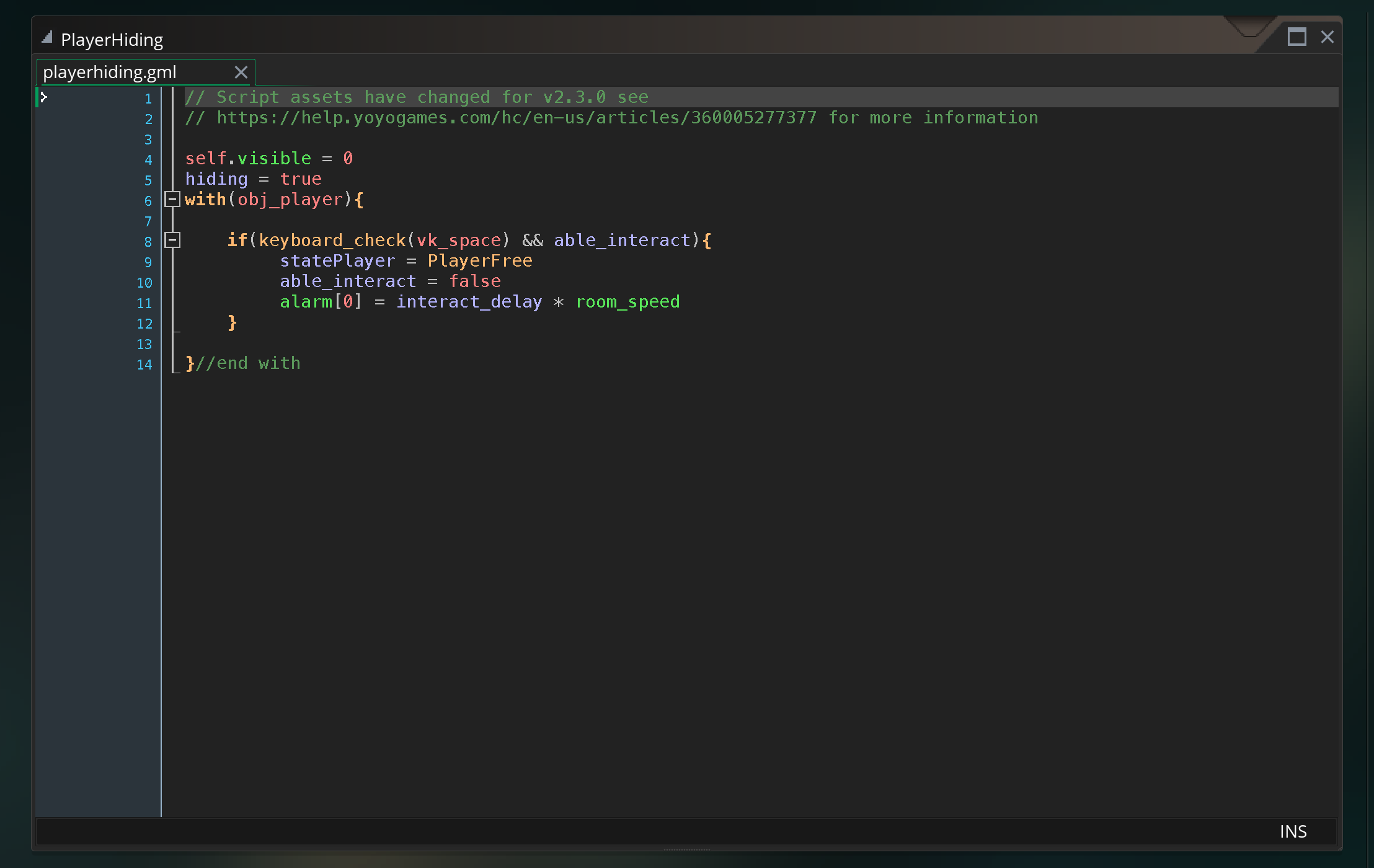
The step event in the player object calls the statePlayer script variable which holds whatever state the player is in. That script is, essentially, acting as the body of the step event of the player. Each script sets properties in the player, allows for various inputs and actions, and transitions based on those inputs to the next state.
Overall, state machines can be very useful when designing your game. Utilizing state machine logic can be a great way to optimize your code and overall workflow.
ASU Game Certificate Devlog
More posts
- A Guide to Writing a Good Rules DocumentFeb 02, 2024
- How to Write a Sample Play DocumentFeb 02, 2024
- Procedural Generation vs Random GenerationOct 21, 2022
- Tips for Writing a Good Pitch DocumentSep 23, 2022
- Good Debugging PracticesSep 16, 2022
- Integrating Github with Gamemaker StudioSep 02, 2022
Leave a comment
Log in with itch.io to leave a comment.